Minneapolis, Minnesota may have the Final Four, but Iowa has such generous tax benefits for charitable gifts. In fact, in Iowa, donors can receive four amazing tax benefits for charitable gifts. Your March Madness bracket may be busted already, but these benefits are ones you can bank on.
Appreciated, long-term property
For donors and potential donors, the ideal asset for charitable donations will depend on a whole range of factors. But, when donating to charity, one type of asset to seriously consider is appreciated, long-term property. Common examples of such property would include publicly traded stock, real estate, and farmland. First, a couple of terms to be clear on:
- Appreciated: simply means increased in value.
- Long-term: property held for more than one year (e.g., 366 days).
Give now, rather than later
The four tax benefits I’ll outline are only available when the charitable gifts are made during a lifetime. It’s been said, “You should be giving while you are living, so you’re knowing where it’s going.” Many Iowans have philanthropic intentions to donate to their favorite causes eventually, usually at death through their estate plan, will, and testamentary trust. Why not give now? You can have more say about your charitable gifts while you are still alive, and also feel the joy that comes with helping the causes you care about most. Again, there are also lots of good tax reasons for giving now rather than later.

Benefits of gifting appreciated, long-term property
While not celebrated as much as the Final Four, there are four genuinely exciting tax benefits for charitable gifts of appreciated, long-term property.
Double Federal Tax Benefit
When you gift appreciated, long-term property (ALTP) to a charity during lifetime, you may receive a double federal tax benefit. First, you can receive an immediate charitable deduction on your federal income tax, which is equal to the fair market value of the property. Second, assuming, of course, you have owned the property for more than one year, when you donate the property, you avoid the long-term capital gain taxes you would have owed if you sold the property.
Let’s look at a concrete example to make this clearer. Pat owns appreciated, long-term property (such as stocks, real estate, or farmland) with a fair market value of $100,000. Pat wants to use the property to help favorite causes in the local community. Which would be better for Pat–to sell the property and donate the cash, or give the property directly to favorite charities? Assume that the property was originally purchased at $20,000 (basis), Pat’s income tax rate is 35%, and the capital gains tax rate is 20%.

Note: This table is for illustrative purposes only. Only your own financial or tax advisor can advise your personal situation on these matters.
Again, a gift of appreciated, long-term property, made during your lifetime, is doubly beneficial. You receive a federal income tax charitable deduction equal to the fair market value of the property. You also avoid the capital gains tax. In Iowa, there is even a greater potential benefit. You may receive a 25% state tax credit for such charitable gifts, lowering the after-tax cost of your gift even further.
25% Endow Iowa Tax Credit
Under the Endow Iowa Tax Credit program, gifts during lifetime can be eligible for a 25% tax credit. There are three requirements to qualify.
- The gift must be given to, or receipted by, a qualified Iowa community foundation.
- The gift must be made to an Iowa charity.
- The gift must be endowed—that is, a permanent gift. Under Endow Iowa, no more than 5% of the gift can be granted each year. The rest is held by and invested by a local community foundation.
Let’s look again at the case of Pat, who is donating appreciated, long-term property per the table above. If Pat makes an Endow Iowa qualifying gift, the tax savings are very dramatic:
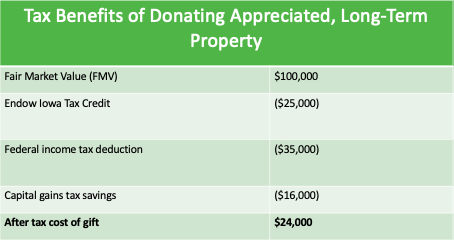
Note: This table is for illustrative purposes only. Only your own financial or tax advisor can advise your personal situation on these matters.
Pat gave a significant and generous gift to a charity of $100,000. But using the Endow Iowa Tax Credit, coupled with the federal income tax charitable deduction and capital gains savings, the after-tax cost of the gift of $100,000 is less than $20,000. Plus, because the gift was endowed, it will be invested by Pat’s local community foundation and will presumably grow through its investment. Thus, it will continue benefiting the charities Pat cares about most!
Note again Pat’s huge tax savings. In this scenario, by giving appreciated, long-term property during lifetime, Pat receives $35,000 as a federal charitable deduction, avoids $16,000 of capital gains taxes, and gains a $25,000 state tax credit, for a whopping total tax savings of $76,000.
Gift Tax Considerations
Yet another benefit: charitable gifts are exempt from federal gift tax. In fact,
charitable contributions made to qualifying charities are not the only deductible on itemized tax returns, but you may also deduct the value of your charitable donations from any amount of gift taxes you owe.
Areas of Caution
Going back to our example, this is a great deal for Pat and a great deal for Pat’s favorite causes. But, could anything go wrong with this scenario? There are a few areas of caution.
Charitable Deduction Capped
The federal income tax charitable deduction is capped. Generally, the federal charitable deduction for gifts of an appreciated, long-term property is limited to 50% of your adjusted gross income (AGI) to public charities and 30% of AGI to private foundations. You may, however, carry forward any unused deduction amount for an additional five years.
Endow Iowa Capped
Endow Iowa Tax Credits are also capped both statewide and per individual. Iowa sets aside a pool of money for Endow Iowa Tax Credits and it is first come, first served. In 2018, approximately $6 million in tax credits were available annually through Endow Iowa. This means it’s not only is it important to make your gift but to fill out and return your Endow Iowa application as quickly as possible. Donors who do not receive tax credits in the year the gift is made will be first in line for the new supply of the next tax year’s credits. (Here’s the 2019 Endow Iowa Tax Credit Application.)
There is also a cap on Endow Iowa tax credit per individual. Tax credits of 25% of the gifted amount are limited to $300,000 in tax credits per individual for a gift of $1.2 million, or $600,000 in tax credits per couple for a gift of $2.4 million (if both are Iowa taxpayers). (Since the inception of the Endow Iowa Tax Credit Program, Iowa Community Foundations have leveraged more than $215 million in permanent endowment fund gifts!)
IRS Requirements for Non-Cash Gifts
Additionally, to receive a charitable deduction for non-cash gifts of more than $5,000, you need a “qualified appraisal” by a “qualified appraiser,” two terms with very specific meanings to the IRS. You need to engage the right professionals to be sure all requirements are met. A notable exception to the appraisal requirement is appreciated long-term, publicly traded stock.
Advice Needs to be Individualized
Finally, all individuals, families, businesses, and farms are unique and have unique tax issues. This article is presented for informational purposes only, not as tax advice or legal advice. Make a fast break to consult a legal professional for personal advice.
All of this can be a bit confusing as you’re working out your planned giving strategy. Do not hesitate to contact me and we can work together to maximize your tax-wise giving.







